LA-14® AND HN001™ INFORMATION
Study aim
To evaluate the changes in Nugent score in women with intermediate vaginal microbiota treated with oral Lactobacillus acidophilus La-14® and Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001™ mixture, in combination with bovine lactoferrin RCX™ (Respecta®) or placebo, for 15 days.
Study design
Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled
Study method
- 40 women with an intermediate Nugent score, indicating a perturbed vaginal microbiota, and with signs/symptoms of vaginitis/vaginosis were randomized to two treatment groups:
- Placebo
- La-14® and HN001™ 5 billion CFU/day with 50 mg of lactoferrin (Respecta®) (Probiotic Combo)
- Lactobacillus species were analyzed by RT-PCR from vaginal swabs at baseline and at the end of the 15-day probiotic/placebo treatment
Study results
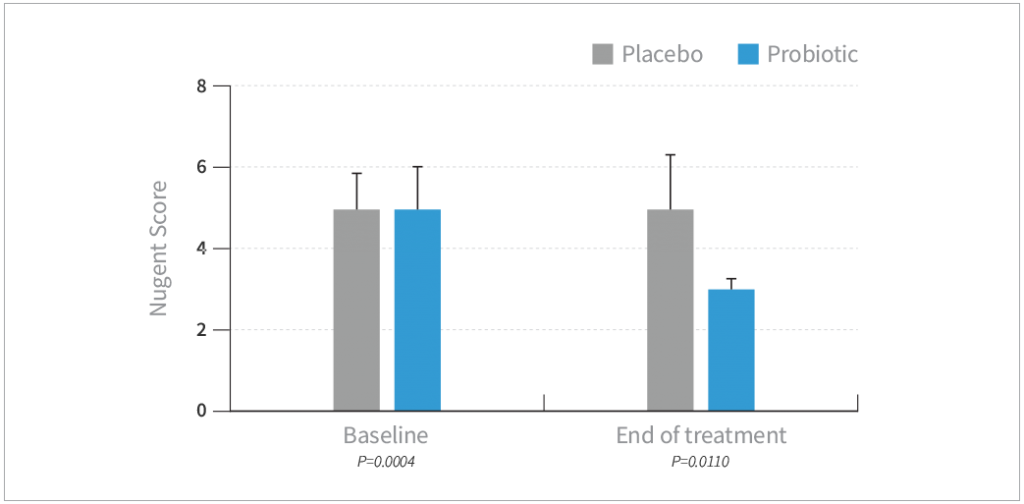
- There was a significant improvement from intermediate to normal Nugent score in the probiotic combo from baseline (P=0.0004)
- No changes from the baseline in the placebo group were found in the Nugent score
- The Nugent score was significantly improved for the probiotic combo group compared with the placebo group (P=0.011) at the end of the treatment
- Vaginal symptoms (itching/discharge) decreased significantly in the probiotic combo group compared to the placebo group (P<0.001)
Evidence-based mixture containing Lactobacillus strains and lactoferrin to prevent recurrent bacterial vaginosis: a double blind, placebo controlled, randomized clinical trial.2
Study aim
To assess the efficacy of L. acidophilus La-14® and L. rhamnosus HN001™, in combination with lactoferrin as adjuvant therapy to metronidazole in women with recurrent bacterial vaginosis (BV).
Study design
Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled
Study method
- 48 women with symptomatic BV infections were treated with metronidazole (500 mg twice daily) for 7 days and were randomly assigned to take simultaneously orally either:
- Placebo
- La-14® and HN001™ with lactoferrin (50 mg)
- An initial induction phase consisted of two capsules/day for five days (10 billion CFU) followed by one capsule/day for 10 consecutive days (5 billion CFU)
- One capsule/day for 10 consecutive days was repeated monthly (maintenance phase) during the 6 months of follow-up starting the first day of menstrual cycle, as the menstrual blood increases the vaginal pH and contributes to an increased risk of BV recurrences
- The clinical cure rate of BV symptoms, microbiological cure rate (Nugent score), and BV recurrence was evaluated during the 6-month study period
Study results
La-14® and HN001™ were associated with significant improvement in recurrent BV symptoms
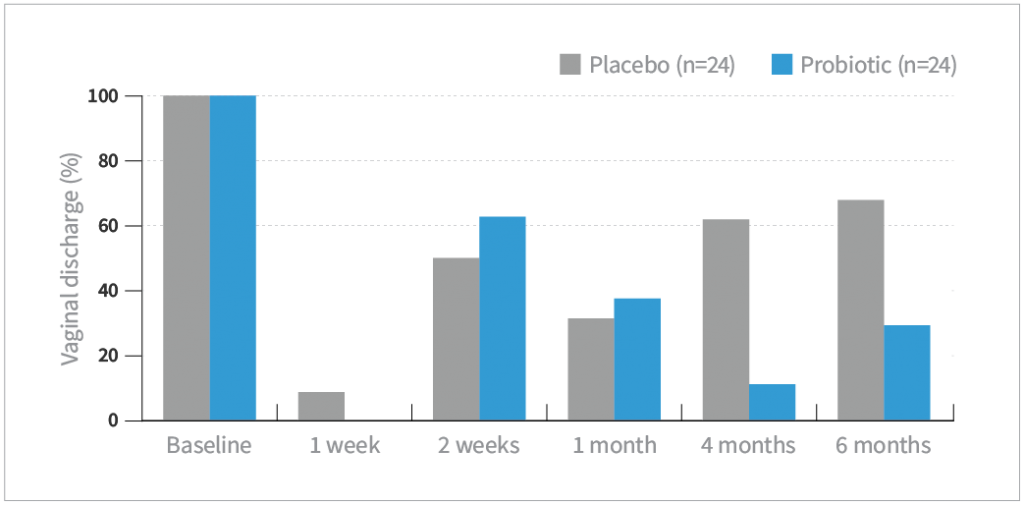
Vaginal discharge
Itching
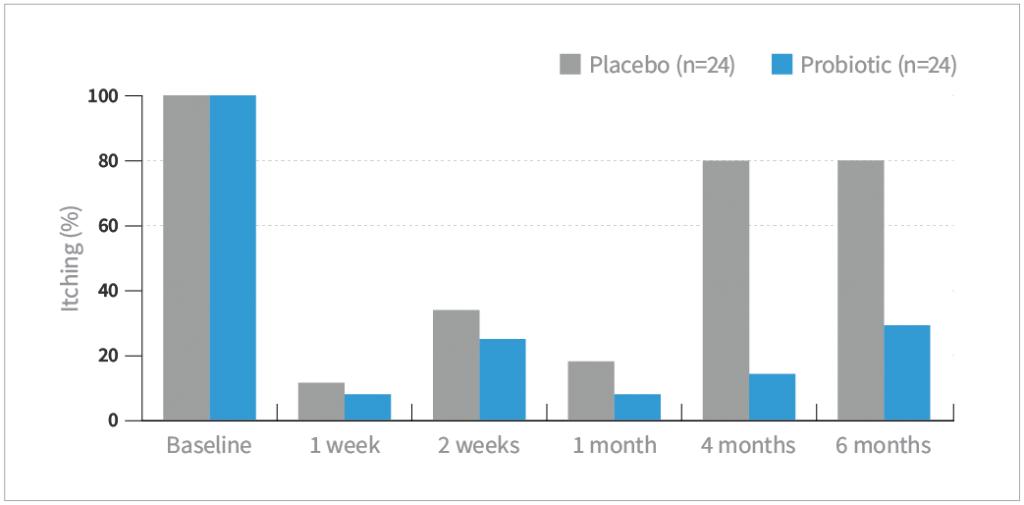
- Based on patient-assessed symptoms (absent or present), there were significant improvements in both vaginal discharge and itching after 4 and 6 months of treatment compared with placebo (P<0.05)
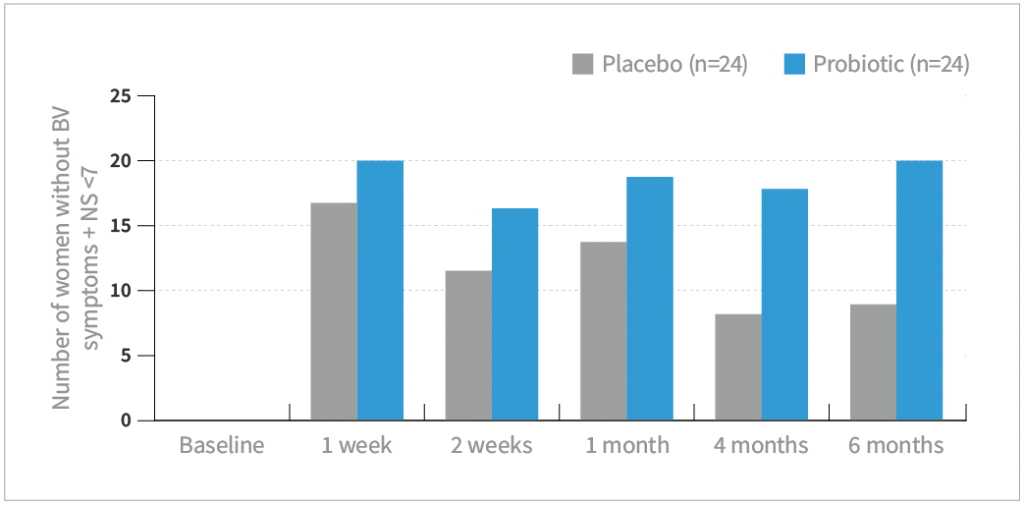
- La-14® and HN001™ significantly improved overall cure rate (absence of symptoms and Nugent score <7) at every time point compared with placebo (P<0.01)
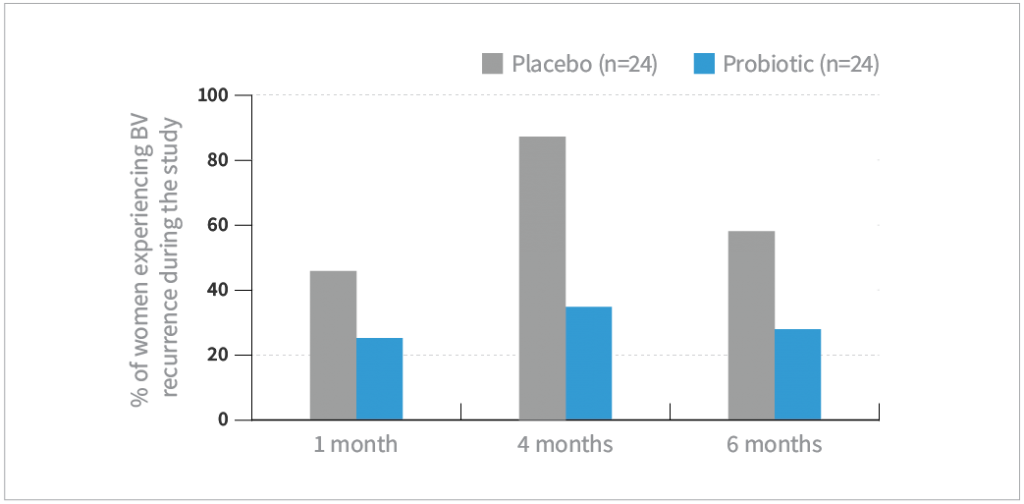
- La-14® and HN001™ was associated with a significant reduction in the rate of BV recurrence (BV symptoms and Nugent score >3) at 1, 4, and 6, months of follow-up compared with placebo (P<0.05)
Randomized clinical trial in women with Recurrent Vulvovaginal Candidiasis: efficacy of probiotics and lactoferrin as maintenance treatment.3
Study aim
To assess the efficacy of L. acidophilus La-14®, L. rhamnosus HN001™, and lactoferrin on symptoms and recurrence of vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC) as adjuvant therapy to topical clotrimazole.
Study design
Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled
Study method
- 48 adult women with symptomatic acute episodes of VVC and a documented anamnestic history of recurrences were treated with a topical clotrimazole (100 mg) for seven days and were randomly assigned to simultaneously orally take either:
- Placebo
- La-14® and HN001™ with lactoferrin (50 mg)
- An initial induction phase consisted of two capsules/day for five days (10 billion CFU) followed by one capsule/day for 10 consecutive days (5 billion CFU)
- One capsule/day for 10 consecutive days was repeated monthly (maintenance phase) during the 6 months of follow-up in the premenstrual phase or luteal phase, as during this time, hormonal and immunological reasons make the vagina more vulnerable to pathogens and pose a higher risk of VVC recurrences
- Symptoms, overall cure rate, and recurrence rate were assessed
Study results
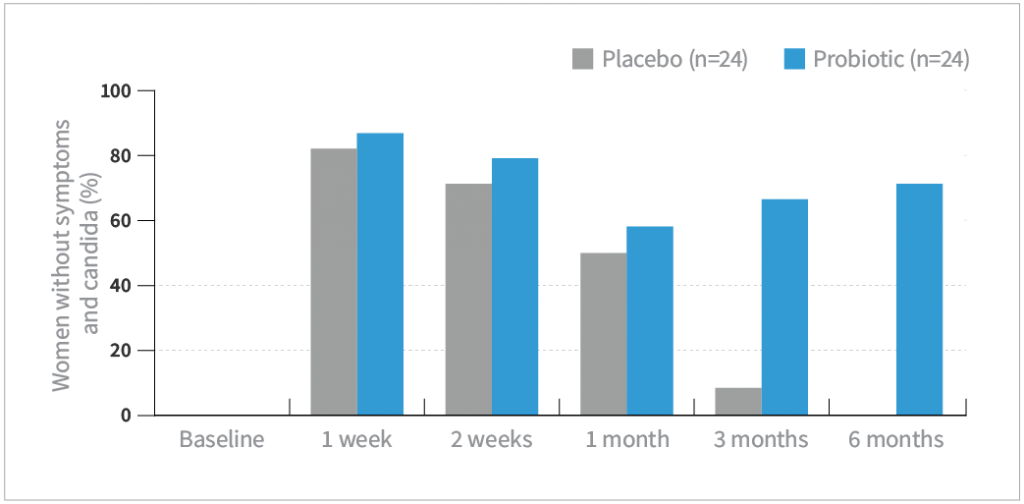
- Absence of VVC was defined as an absence of symptoms and negative candida culture
- The probiotic combo significantly increased the VVC cure rate compared to placebo at 3 and 6 months of follow-up (P<0.01)
La-14® and HN001™ probiotic combo was associated with a significant improvement of itching and vaginal discharge at 3 and 6 months (P<0.01) (Data not shown)
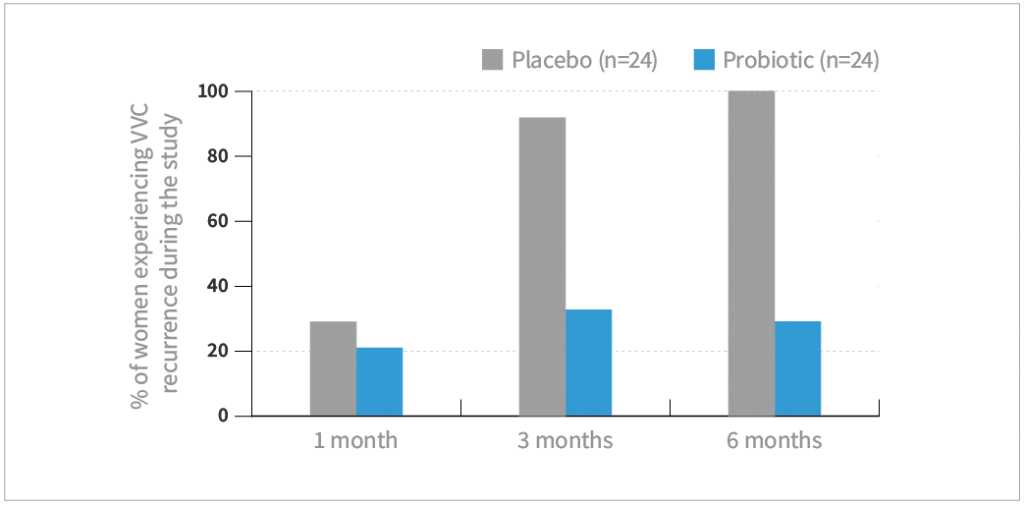
- VVC recurrence rate was defined as the presence of at least 1 symptom and positive candida culture
- During the six-month follow-up, the VVC recurrence rate was significantly less in the probiotic group vs placebo at 3 and 6 months follow-up (P<0.01)
Vaginal Colonization Data
Study aim
To determine if Lactobacillus acidophilus La-14® and Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001™ could be detected in the vaginas of healthy women once consumed.
Study design
Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled pilot study
Study method
- 40 healthy women were randomized to two treatment groups:
- Placebo (100 mg maltodextrin)
- La-14® and HN001™ 10 billion CFU/day with lactoferrin
- Vaginal swabs were taken at 0, 7, 14, and 21 days and analyzed by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) for detection and quantification of DNA of L rhamnosus and L acidophilus
- Vaginal pH was also measured
Study results
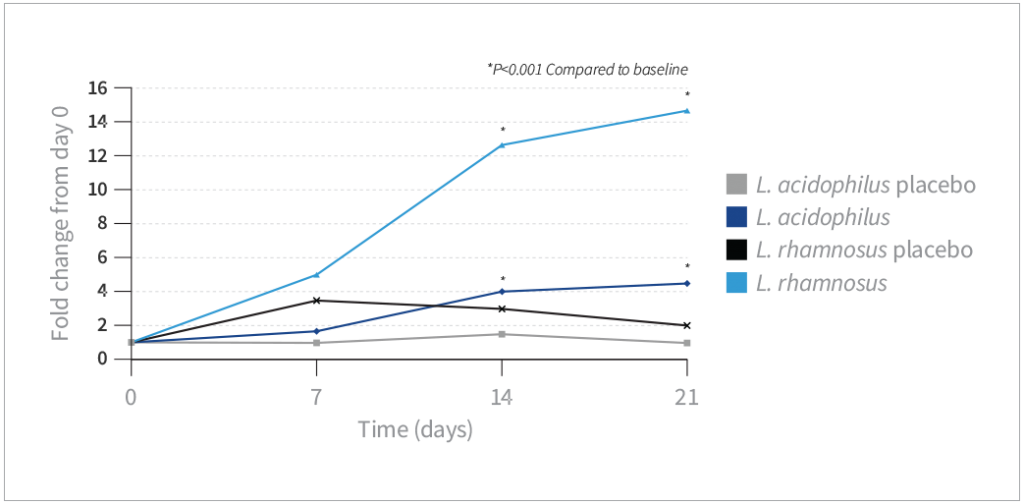
- Compared to baseline, vaginal L. acidophilus levels were significantly increased on days 14 and 21 in the probiotic group (P<0.001).
- Compared to baseline, vaginal L. rhamnosus levels were increased on days 14 and 21 in the probiotic group (P<0.001)
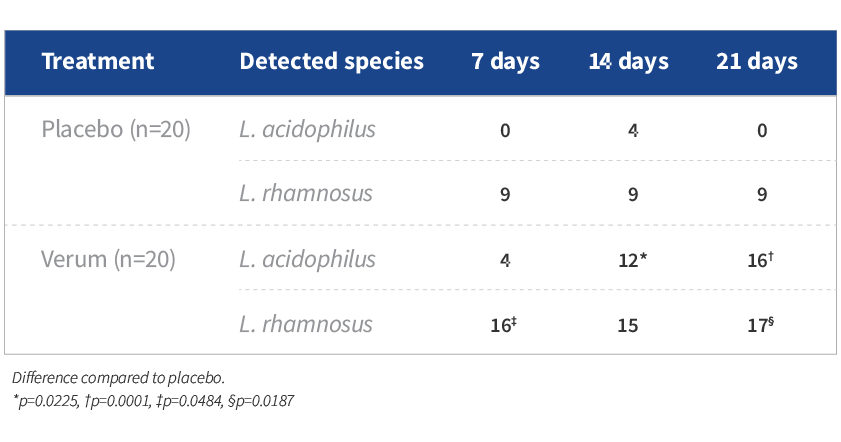
- Transient colonization of L. acidophilus (ie, at least double levels from baseline) was observed on days 14 and 21 in 12 (P=0.0225) and 16 (P=0.0001) out of 20 women, respectively, in the probiotic combo group
- Transient colonization of L. rhamnosus was observed on days 7 and 21 in 16 (P=0.0484) and 17 (P=0.0187) out of 20 women, respectively, in the probiotic combo group
- No significant transient colonization was found in the placebo group
REFERENCES:
1. Russo R, Edu A, De Seta F. Study on the effects of an oral lactobacilli and lactoferrin complex in women with intermediate vaginal microbiota. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2018;298(1):139-145. doi: 10.1007/s00404-018-4771-z. 2. Russo R, Karadja E, De Seta F. Evidence-based mixture containing Lactobacillus strains and lactoferrin to prevent recurrent bacterial vaginosis: a double blind, placebo controlled, randomised clinical trial. Benef Microbes. 2019;10(1):19-26. doi: 10.3920/BM2018.0075. 3. Russo R, Superti F, Karadja E, De Seta F. Randomised clinical trial in women with Recurrent Vulvovaginal Candidiasis: Efficacy of probiotics and lactoferrin as maintenance treatment. Mycoses. 2019;62(4):328-335. doi: 10.1111/myc.12883. 4. De Alberti D, Russo R, Terruzzi F, Nobile V, Ouwehand AC. Lactobacilli vaginal colonisation after oral consumption of Respecta® complex: a randomised controlled pilot study. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2015;292(4):861-867
