Prenatal support
Study aim
To assess whether supplementation with the probiotic L. rhamnosus HN001™ can be associated with a reduction of the prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM).
Study design
Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled parallel trial
Study method
- 373 pregnant women with a personal or partner history of atopic disease were randomized at 14 to 16 weeks gestation to receive:
- Placebo
- HN001™ (6 billion CFU)
- GDM at 24 to 30 weeks was assessed using the definition of the International Association of Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups (IADPSG) (fasting plasma glucose ≥5.1 mmol/l, or 1 hr post 75-g glucose level at ≥10 mmol/l or at 2 hr ≥8.5 mmol/l) and NZ definition (fasting plasma glucose ≥5.5 mmol/l or 2 hr post 75-g glucose at ≥9 mmol/l)
- All analyses were intention-to-treat
Study results
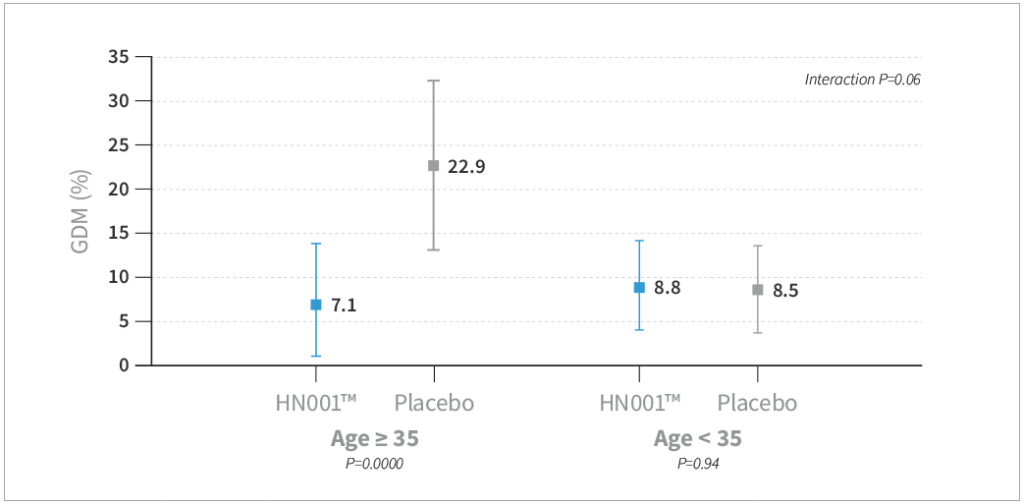
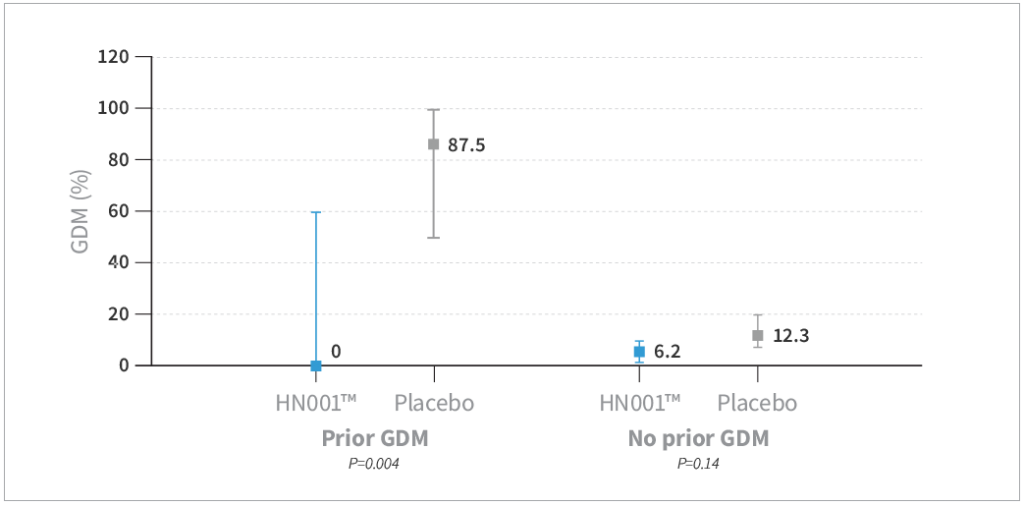
- HN001™ supplementation resulted in a trend toward reduced risk of GDM by IADPSG criteria compared to placebo by 40% (P=0.08) and a significantly lower level of GDM by 68% compared to placebo when assessed by the New Zealand definition (P=0.03)
- GDM was lower in the HN001™ group compared to placebo, specifically in mothers older than 35 years of age (P=0.009) and mothers with a history of GDM (P=0.004)
- Fasting blood glucose levels were slightly lower in the HN001™ group (P=0.048)
Postnatal support
Study aim
To evaluate the effect of L. rhamnosus HN001™ given in pregnancy and postpartum on symptoms of maternal depression and anxiety in the postpartum period. (This was a secondary outcome; the primary outcome was offspring eczema at 12 months of age.)
Study design
Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled
Study method
- 423 women at 14 to 16 weeks gestation were randomized to:
- Placebo
- HN001™ (6 billion CFU)
- Women were randomized to receive either placebo or HN001™ daily from enrollment until 6 months postpartum if breastfeeding
- Modified versions of the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale and State Trait Anxiety Inventory were used to assess symptoms of depression and anxiety postpartum
- 380 women (89.8%) completed the questionnaire on psychological outcomes, 193 (91.0%) in the treatment group, and 187 (88.6%) in the placebo group
Study results

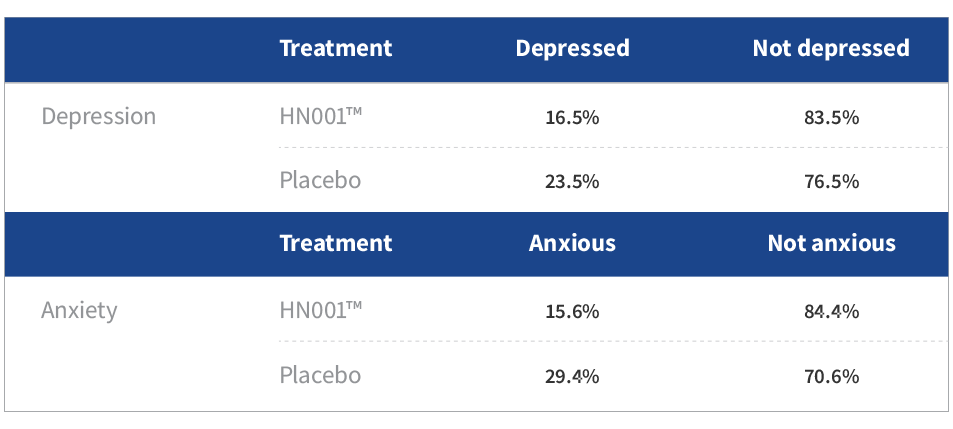
- Mothers taking HN001™ reported significantly lower depression and anxiety scores than those in placebo (P<0.05)
REFERENCES:
1. Wickens KL, Barthow CA, Murphy R, et al. Early pregnancy probiotic supplementation with Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 may reduce the prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus: a randomised controlled trial. Br J Nutr. 2017;117(6):804-813. 2. Slykerman RF, Hood F, Wickens K, et al. Effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 in pregnancy on postpartum symptoms of depression and anxiety: A randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial. EBioMedicine. 2017;24:159-165.
