Probiotic effects on cold and influenza-like symptom incidence and duration in children.1
Study aim
To determine the effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM® or L. acidophilus NCFM® in combination with Bifidobacterium animalis subsp lactis Bi-07™ on cold and influenza-like symptom incidence and duration in healthy children during the winter season (November to May).
Study design
Double-blind, placebo-controlled
Study method
- 326 eligible children (3-5 years of age) were assigned randomly to receive:
- Placebo
- NCFM® 10 billion CFU
- NCFM® 5 billion CFU and Bi-07™ 5 billion CFU
- Children were treated twice daily for 6 months
- Cold- and flu-like symptoms (fever, cough, rhinorrhea) and other symptoms were monitored for frequency and duration
- The incidence of illness-related or flu-like symptoms and the number of absences from day care due to illness were also recorded
Study results
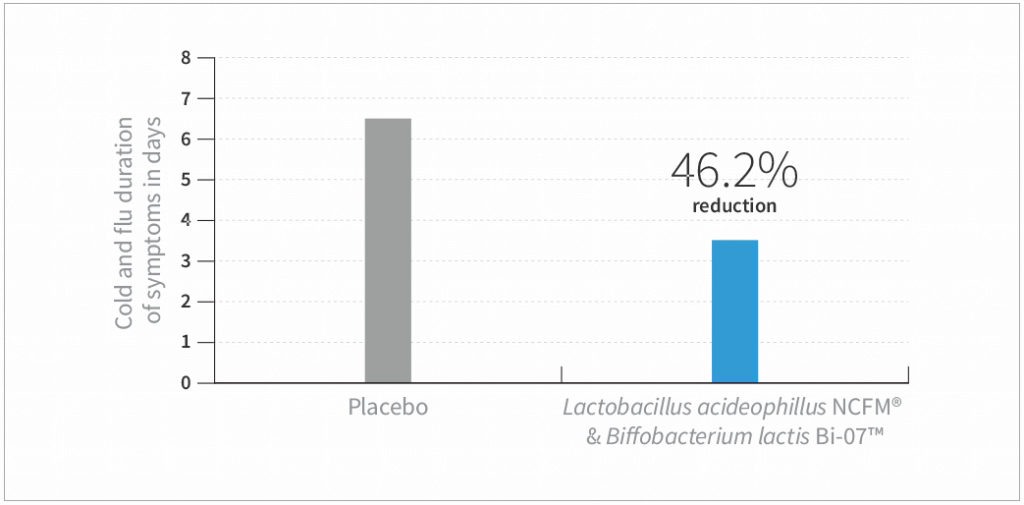
- The cumulative number of symptom days was significantly reduced by nearly half (or approximately 3 days) in the probiotic group compared to placebo (P<0.001)
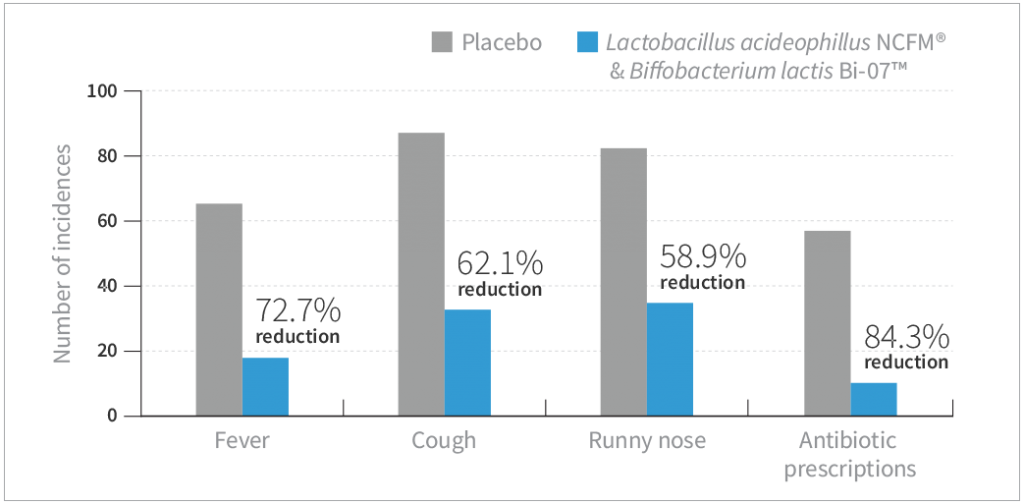
- Results showed a significant reduction in fever, cough, runny nose, and antibiotic usage in the probiotic group compared to placebo (P≤0.03)
*Results reported are from placebo and NCFM® and Bi-07™ combination; NCFM® alone results not shown.
REFERENCE:
1. Leyer GJ, Li S, Mubasher ME, Reifer C, Ouwehand AC. Probiotic effects on cold and influenza-like symptom incidence and duration in children. Pediatrics. 2009;124(2):e172-179.
