Study aim
To determine the dose-response effect of HOWARU® HN019™ formulation on the reduction of colonic transit time in healthy adults with functional gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms
Study design
14-day, triple-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled
Study method
- 100 patients randomized to 3 treatment groups:
- Placebo
- HOWARU® HN019™ low dose (1.8 billion CFU/day)
- HOWARU® HN019™ high dose (17.2 billion CFU/day)
- Transit time was assessed by X-ray on days 0 and 14 following 6 days of ingestion of capsules containing radio-opaque markers
- The frequency of gurgling, nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, flatulence, constipation, regurgitation, abdominal pain, and irregular bowel movements were assessed by a questionnaire on a scale from 0 (never) to 100 (always)
Study results
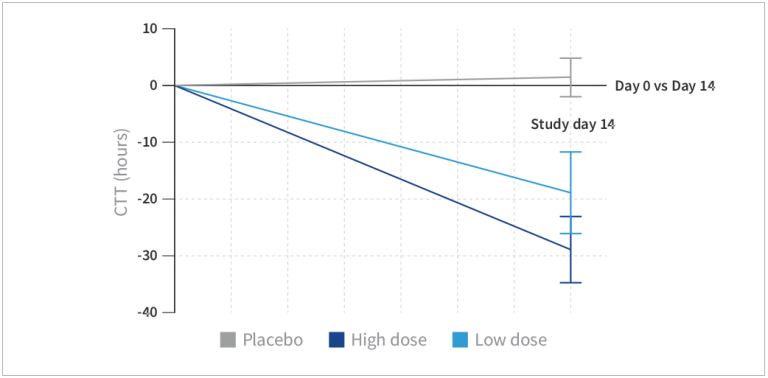
Change in colonic transit time over 14 days by study group. Values represent mean ± 95% confidence interval.
- Subjects taking low-dose HN019™ experienced a better transit time with a reduction of almost 18 hours (P=0.01) compared to placebo.
- Subjects taking high-dose HN019™ experienced a colonic transit time reduction of 28 hours (P<0.001) compared to placebo.
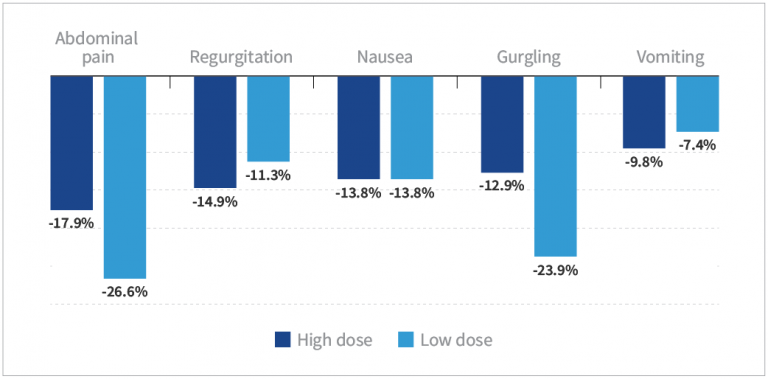
- Subjects taking low- and high-dose HN019™ experienced significantly reduced symptoms from baseline (P<0.05), except for vomiting in the low-dose group
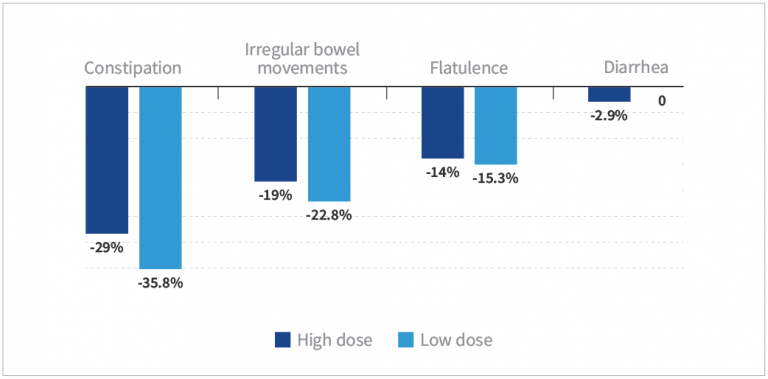
- Subjects taking low- and high-dose HN019™ experienced significantly reduced symptoms from baseline (P<0.05), except for diarrhea in both the low- and high-dose groups
REFERENCE:
1. Waller PA, Gopal PK, Leyer GJ, et al. Dose-response effect of Bifidobacterium lactis HN019™ on whole gut transit time and functional gastrointestinal symptoms in adults. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2011;46(9):1057–1064.
