Study aim
To determine the dose-response effect of HOWARU® Restore formulation (Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM®; Lactobacillus paracasei Lpc-37™; Bifidobacterium lactis Bi-07™; Bifidobacterium lactis Bl-04®) on the incidence of antibiotic associated diarrhea (AAD) and C. difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) and severity of gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms in adults receiving antibiotic therapy.
Study design
Triple-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled
Study method
503 patients randomized to 3 treatment groups
- Placebo
- Low dose (4.17 billion CFU)
- High dose (17 billion CFU)
Study results
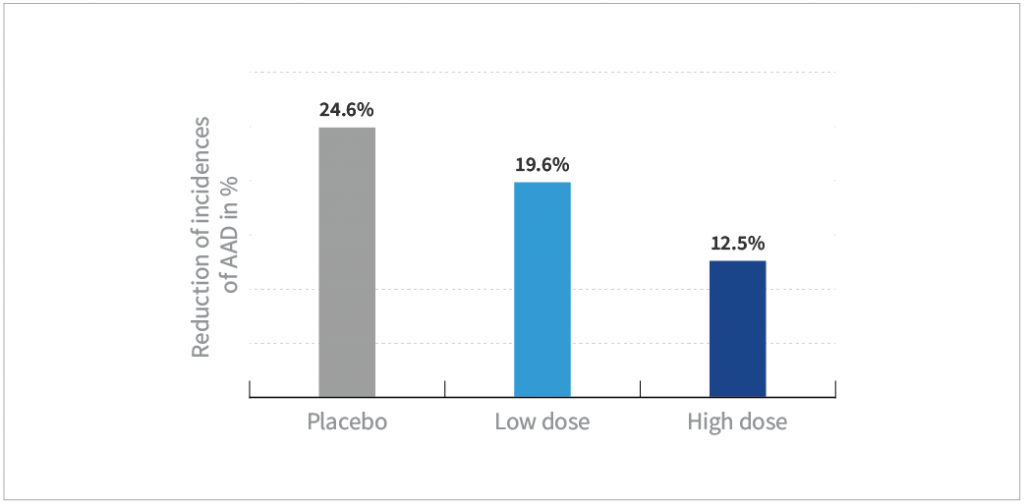
- The incidence of AAD in the high-dose HOWARU® Restore group was approximately half that of subjects in the placebo group (P=0.005)
- Subjects taking the low-dose HOWARU® Restore treatment experienced a lower incidence of AAD compared to placebo group, but the results were not statistically significant (P=0.08)
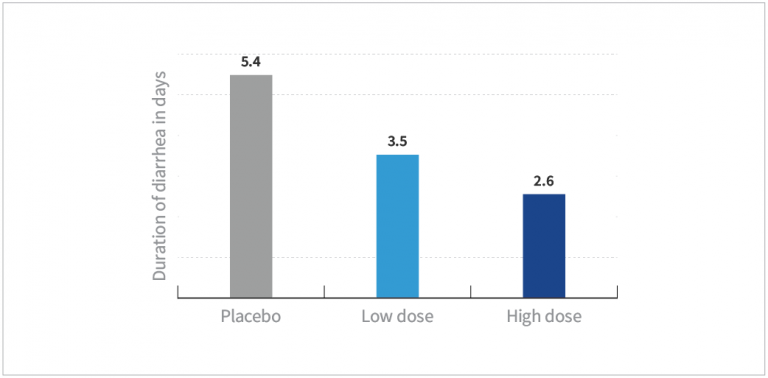
- HOWARU® Restore at both the low dose and high dose was shown to significantly reduce the duration of diarrhea by approximately 2 to 3 days compared to placebo (P<0.001)
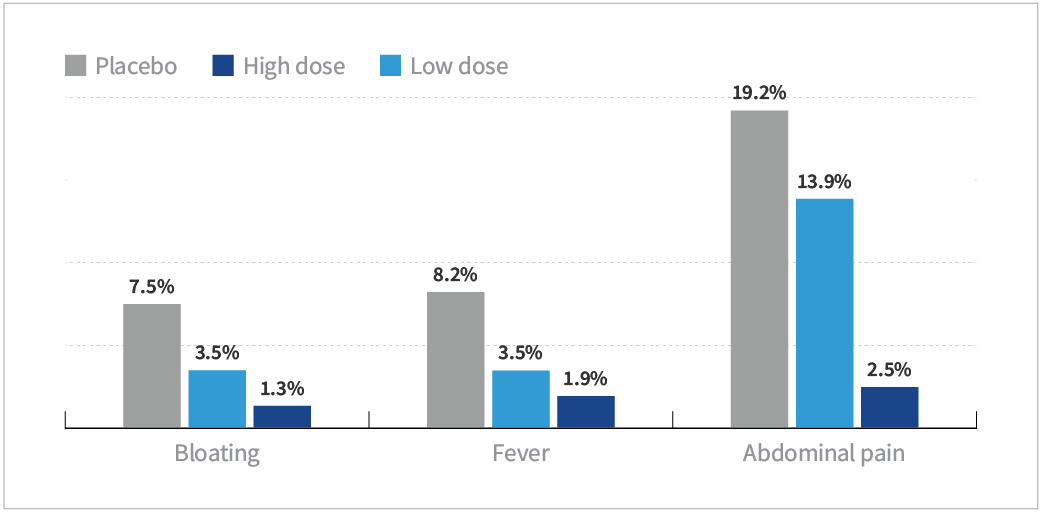
HOWARU® Restore demonstrated an impact on undesirable GI symptoms during antibiotic therapy compared to placebo with:
- A significant reduction of abdominal pain for both groups (high dose: P<0.001; low dose: P=0.001)
- A significant reduction of bloating for the high group (P=0.01) with a significant linear dose-response trend (P=0.008)
- A significant reduction of fever in the high-dose group (P=0.02) with a trend toward fewer cases of fever in the low-dose group (P=0.09)
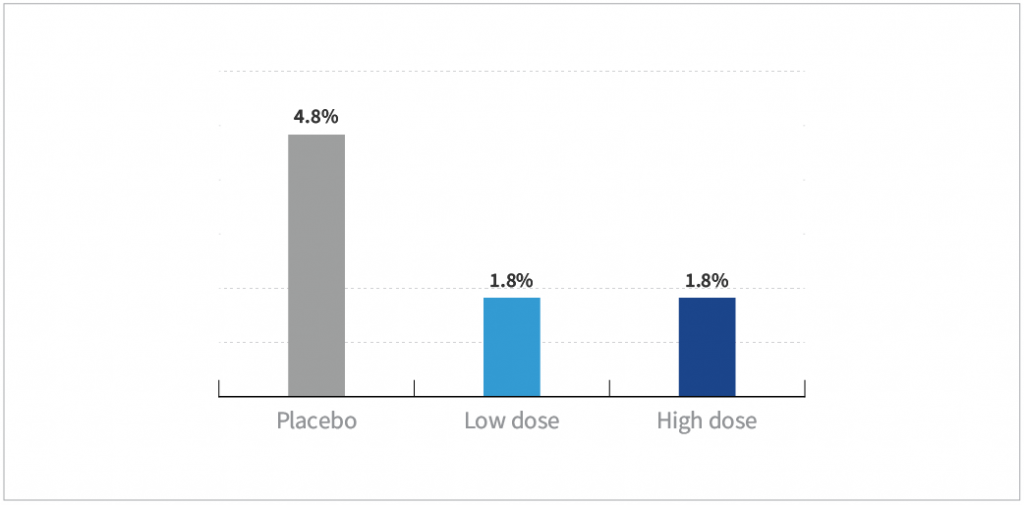
- Subjects taking the high dose of HOWARU® Restore had a significantly reduced incidence of CDAD (P=0.02)
Study aim
To determine if HOWARU® Restore formulation (Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM®; Lactobacillus paracasei Lpc-37™; Bifidobacterium lactis Bi-07™; Bifidobacterium lactis Bl-04®; Bifidobacterium bifidum Bb-02™) could minimize antibiotic-induced disruption of fecal microbiota and facilitate its return to the baseline in healthy volunteers.
Study design
Randomized, placebo controlled
Study method
51 subjects randomized to 2 treatment groups:
- Placebo
- HOWARU® Restore (41 billion CFU/day)
- Subjects also received amoxicillin/ clavulanic acid (875 mg twice per day)
Subjects completed a diary recording stool frequency, gastrointestinal symptoms, and overall well-being throughout the protocol.
Study results
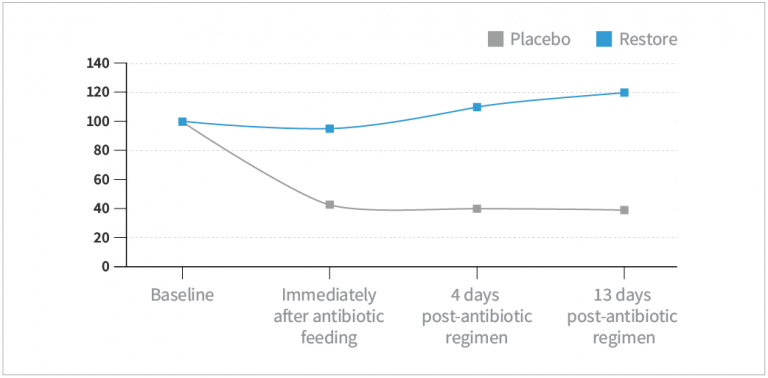
- Subjects in the HOWARU® Restore group experienced a rapid re-establishment of bifidobacterial levels while placebo shows no improvement 2 weeks after cessation of gut stress (P=0.03).
REFERENCES:
1. Ouwehand AC, DongLian C, Weijian X, et al. Probiotics reduce symptoms of antibiotic use in a hospital setting: a randomized dose response study. Vaccine. 2014;32(4):458-463. 2. Engelbrektson A, Korzenik JR, Pittler A, et al. Probiotics to minimize the disruption of faecal microbiotia in healthy subjects undergoing antibiotic therapy. J Medical Microbiology. 2009;58:663-670.
